Understanding Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain

Shoulder internal rotation pain is a common yet often misunderstood condition that can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the intricacies of shoulder pain, particularly in terms of internal rotation, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and ways to prevent it. With a better understanding of the condition, individuals can take actionable steps towards recovery and enhanced functionality.
What is Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain?
Shoulder internal rotation pain refers to discomfort experienced during the internal rotation of the shoulder joint. This pain can manifest during specific activities, such as reaching behind your back or lifting objects above your head. The shoulder joint is a complex structure that consists of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, all of which can contribute to pain when they are overstressed or injured.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Shoulder
To comprehend shoulder internal rotation pain, it is crucial to understand the anatomy of the shoulder:
- Bones: The shoulder is made up of three major bones—the humerus, scapula, and clavicle.
- Muscles: Key muscles involved in shoulder movement include the rotator cuff muscles, deltoid, and pectoral muscles.
- Tendons: Tendons connect muscles to bones and play a significant role in shoulder movement.
- Ligaments: Ligaments connect bones to other bones and provide stability to the shoulder joint.
Causes of Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain
Understanding the various causes of shoulder internal rotation pain can help in devising effective treatment plans. Common causes include:
- Rotator Cuff Injuries: Tears or inflammation in the rotator cuff can lead to pain during internal rotation.
- Shoulder Impingement: This occurs when shoulder muscles catch on the shoulder blade, causing pain and restricted movement.
- Arthritis: Conditions such as osteoarthritis can lead to inflammation and pain in the shoulder joint.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that reduces friction, can cause pain during shoulder movements.
- Injuries: Trauma from falls or accidents can damage shoulder structures, leading to pain and dysfunction.
- Posture-Related Issues: Poor posture can lead to muscle imbalances and contribute to shoulder pain.
Symptoms of Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain
The symptoms associated with shoulder internal rotation pain can vary in intensity and duration, and they often include:
- Localized Pain: Pain may be confined to the shoulder area, specifically during internal rotation.
- Stiffness: Individuals may experience reduced range of motion or stiffness in the shoulder joint.
- Weakness: Difficulty lifting objects or performing overhead activities may occur.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the shoulder area can lead to noticeable swelling.
- Cracking or Popping Sounds: Movements of the shoulder joint may produce unusual sounds.
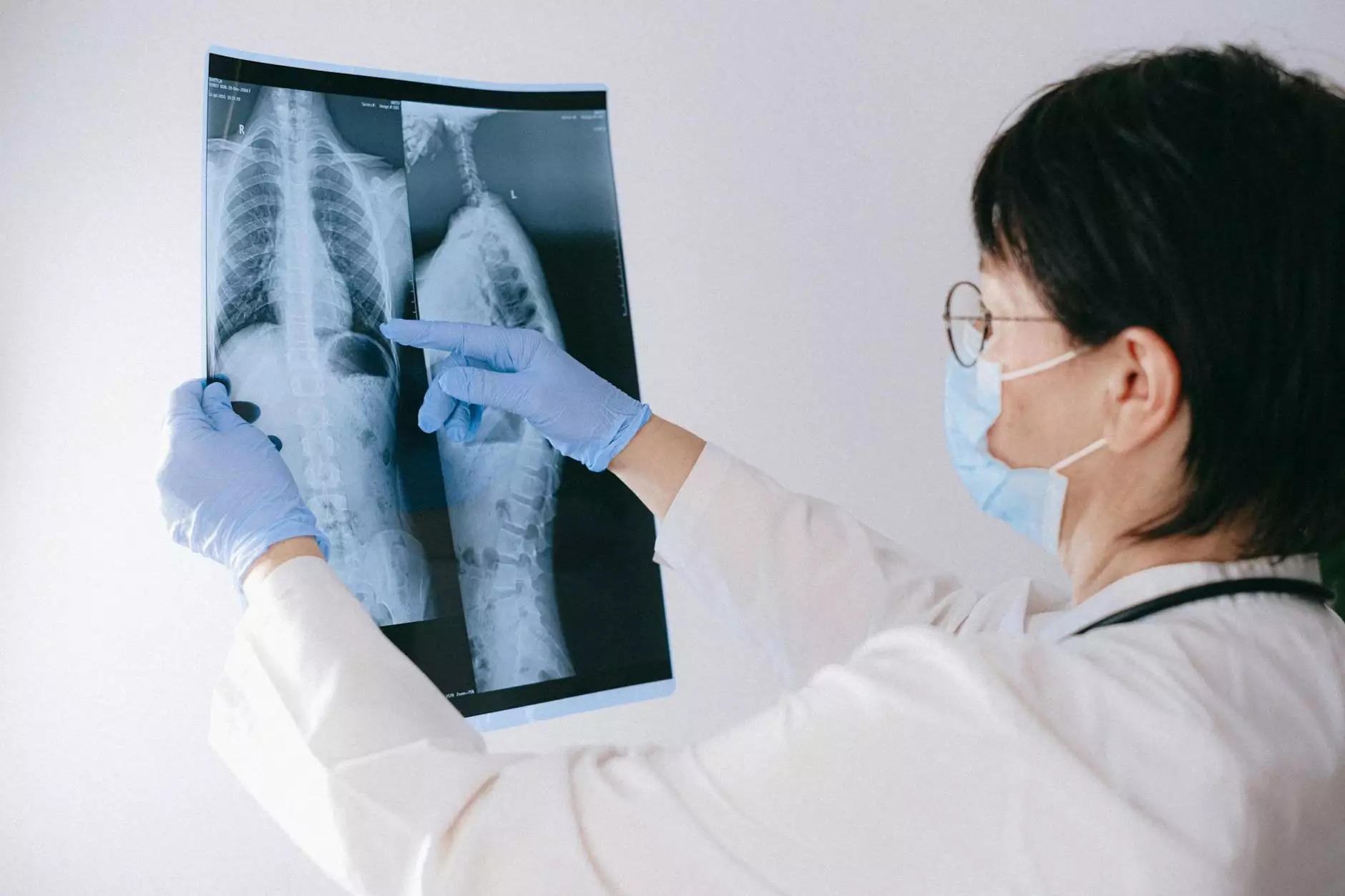
Diagnosis of Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Healthcare professionals use various methods to diagnose shoulder internal rotation pain, including:
- Medical History Review: Understanding the patient's history and symptoms is vital.
- Physical Exam: Doctors perform physical examinations to assess the range of motion, strength, and areas of pain.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasound may be used to visualize the shoulder and identify any underlying injuries.
- Functional Testing: Assessing the functionality of the shoulder through specific movements may also aid in diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain
Treatment for shoulder internal rotation pain often depends on the underlying cause, severity, and individual patient needs. Common treatment options include:
1. Conservative Treatments
- Rest: Allowing the shoulder to rest can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs can alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises can improve strength, flexibility, and functionality of the shoulder.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications such as ibuprofen can help manage pain and inflammation.
2. Advanced Treatments
- Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: This emerging treatment involves injecting platelets from the patient's blood into the injury site to promote healing.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical interventions such as rotator cuff repair or shoulder arthroscopy may be necessary.
Prevention of Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain
Preventing shoulder internal rotation pain is essential, particularly for individuals already at risk due to their activities or lifestyle. Here are some effective prevention strategies:
- Proper Warm-Up and Stretching: Always warm up before engaging in physical activities to reduce the risk of injury.
- Maintain Good Posture: Practicing good ergonomics in daily activities can help reduce strain on the shoulder.
- Strengthening Exercises: Incorporate exercises that strengthen shoulder and back muscles to provide better support.
- Avoid Repetitive Strain: Limit repetitive overhead motions when possible to prevent overuse injuries.
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine evaluations by healthcare professionals can detect issues before they develop into serious conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, shoulder internal rotation pain is a multifaceted condition that can greatly affect daily activities and overall quality of life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for effective management. It is advisable to seek professional medical advice if you experience persistent shoulder pain to ensure appropriate diagnosis and treatment. By taking proactive steps towards shoulder health, you can enhance your mobility and improve your quality of life.
Additional Resources
For further reading on shoulder health and related conditions, consider exploring resources from reputable organizations and websites such as:
- IAOM - International Academy of Orthopedic Medicine
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- National Center for Biotechnology Information
FAQs About Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain
1. Can shoulder internal rotation pain be caused by sleeping positions?
Yes, poor sleeping positions can lead to shoulder pain, particularly if the arm is positioned awkwardly or if there’s direct pressure on the shoulder.
2. How long does it take for shoulder internal rotation pain to heal?
The healing time for shoulder internal rotation pain varies widely depending on the cause and severity, ranging from a few days to several months.
3. Is physical therapy effective for treating shoulder internal rotation pain?
Yes, physical therapy is often highly effective in treating this condition by improving strength, flexibility, and reducing pain.